概述
数组是所有 JavaScript 程序员非常熟悉和经常使用的数据结构,和其他的语言类似,仅仅通过一个简单的 let foo = [] 就可以创建出一个数组并使用他。但是,作为一种弱类型语言,使用过其他强类型语言的程序员也许会对 javascript 的这种写法感到非常疑惑:let array = [0, 'a', "hello"]。WTF?发生了什么,难道数组里面的元素类型不应该是完全一致的么?这是发生了什么魔法么。
JavaScript 到底是如何构建和管理数组的呢?这篇文章就以 nodejs 依赖的 v8 引擎为例,深入理解 js 管理数组的原理。
注 如果觉得不想读完整篇文章,只想了解大概的内容,可以到文章末尾阅读 小结 章节。
注 为了文章的严谨性,本文采用的是 Nodejs 版本 16.13.0 在提交: 8fdabcb 所依赖的 V8 版本: 9.4.146,其他的版本特性和改动均不再此次讨论的范围内。
JS 的数组定义
首先来看一下 MDN 的文档是怎么定义 JS 中的数组类型的:
The JavaScript Array class is a global object that is used in the construction of arrays; which are high-level, list-like objects.
MDN Array 定义
JS 数组的“类型”
什么?JS 的数组什么时候有了类型?没错,JS 的数组是有类型的,只不过在 JavaScript 的层次,数组的类型是没有意义的。但是在实际的 JavaScript 引擎中,引入类型是非常正常的做法,例如 V8 引擎在实现数组的是后就引入了类型的概念。我们下面来简单介绍一下,在 V8 层面上,数组的类型究竟是怎么实现的。
首先给出下图,这是 V8 定义的 JS 数组类型。
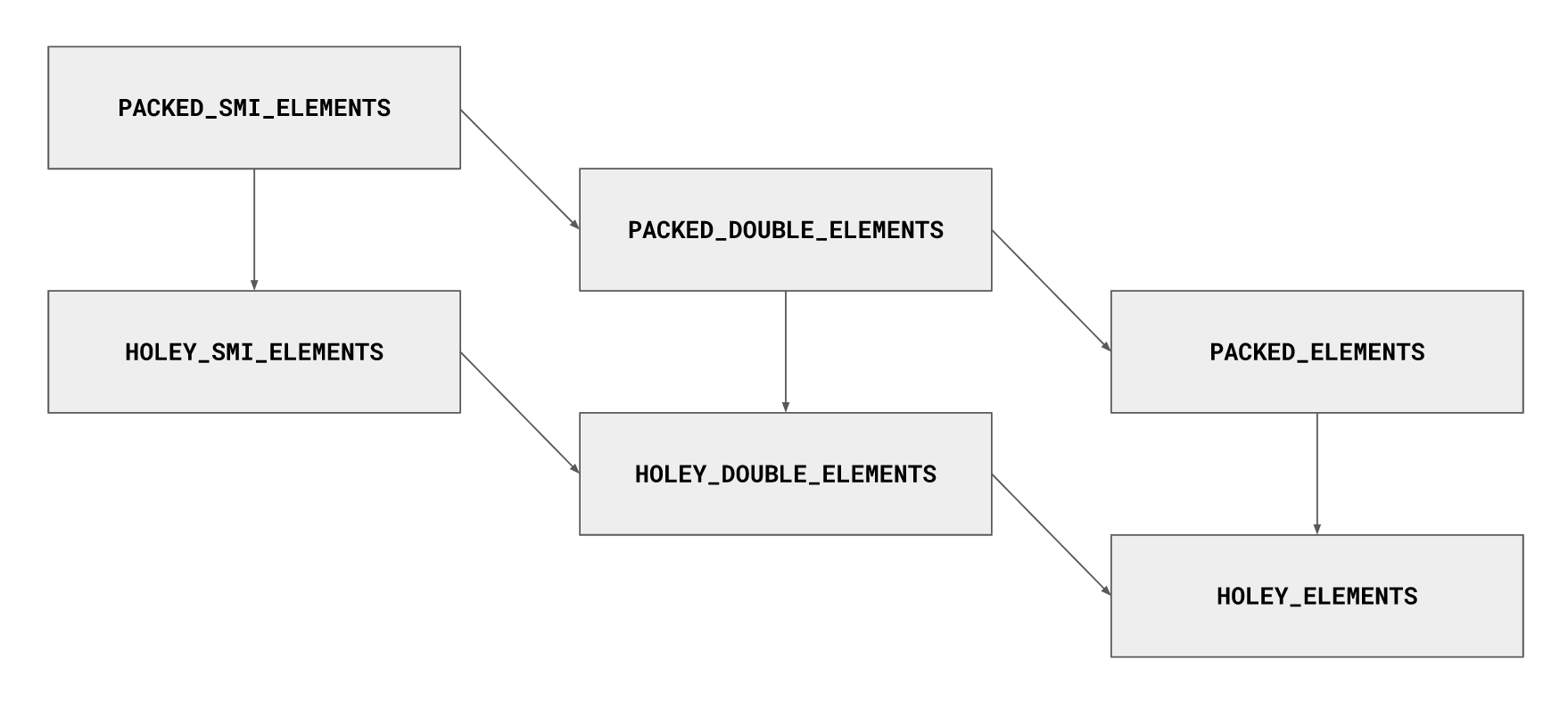
这张图中所展示的类型主要有以下几个特点:
- 所有的类型以
_ELEMENTS 结尾
- 都用下划线分割为了三段
- 第一段有两种值:
PACKED 和 HOLEY
- 第二段有三种值:
SMI 、 DOUBLE 和 ``
我们来对以上四点进行分点解析
这是 V8 中一个很有意思的地方,我把相关的源代码贴在下方:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
|
// elements-kind.h
// The "fast" kind for elements that only contain SMI values. Must be first
// to make it possible to efficiently check maps for this kind.
PACKED_SMI_ELEMENTS,
HOLEY_SMI_ELEMENTS,
// The "fast" kind for tagged values. Must be second to make it possible to
// efficiently check maps for this and the PACKED_SMI_ELEMENTS kind
// together at once.
PACKED_ELEMENTS,
HOLEY_ELEMENTS,
// The "fast" kind for unwrapped, non-tagged double values.
PACKED_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS,
HOLEY_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS,
// The nonextensible kind for elements.
PACKED_NONEXTENSIBLE_ELEMENTS,
HOLEY_NONEXTENSIBLE_ELEMENTS,
// The sealed kind for elements.
PACKED_SEALED_ELEMENTS,
HOLEY_SEALED_ELEMENTS,
// The frozen kind for elements.
PACKED_FROZEN_ELEMENTS,
HOLEY_FROZEN_ELEMENTS,
// The "slow" kind.
DICTIONARY_ELEMENTS,
// Elements kind of the "arguments" object (only in sloppy mode).
FAST_SLOPPY_ARGUMENTS_ELEMENTS,
SLOW_SLOPPY_ARGUMENTS_ELEMENTS,
// For string wrapper objects ("new String('...')"), the string's characters
// are overlaid onto a regular elements backing store.
FAST_STRING_WRAPPER_ELEMENTS,
SLOW_STRING_WRAPPER_ELEMENTS,
// Fixed typed arrays.
#define TYPED_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_KIND(Type, type, TYPE, ctype) TYPE##_ELEMENTS,
TYPED_ARRAYS(TYPED_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_KIND)
RAB_GSAB_TYPED_ARRAYS(TYPED_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_KIND)
#undef TYPED_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_KIND
// WasmObject elements kind. The actual elements type is read from the
// respective WasmTypeInfo.
WASM_ARRAY_ELEMENTS,
// Sentinel ElementsKind for objects with no elements.
NO_ELEMENTS,
// Derived constants from ElementsKind.
FIRST_ELEMENTS_KIND = PACKED_SMI_ELEMENTS,
LAST_ELEMENTS_KIND = RAB_GSAB_BIGINT64_ELEMENTS,
FIRST_FAST_ELEMENTS_KIND = PACKED_SMI_ELEMENTS,
LAST_FAST_ELEMENTS_KIND = HOLEY_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS,
FIRST_FIXED_TYPED_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_KIND = UINT8_ELEMENTS,
LAST_FIXED_TYPED_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_KIND = BIGINT64_ELEMENTS,
FIRST_RAB_GSAB_FIXED_TYPED_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_KIND = RAB_GSAB_UINT8_ELEMENTS,
LAST_RAB_GSAB_FIXED_TYPED_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_KIND = RAB_GSAB_BIGINT64_ELEMENTS,
TERMINAL_FAST_ELEMENTS_KIND = HOLEY_ELEMENTS,
FIRST_ANY_NONEXTENSIBLE_ELEMENTS_KIND = PACKED_NONEXTENSIBLE_ELEMENTS,
LAST_ANY_NONEXTENSIBLE_ELEMENTS_KIND = HOLEY_FROZEN_ELEMENTS,
// Alias for kSystemPointerSize-sized elements
#ifdef V8_COMPRESS_POINTERS
SYSTEM_POINTER_ELEMENTS = PACKED_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS,
#else
SYSTEM_POINTER_ELEMENTS = PACKED_ELEMENTS,
#endif
|
可以看到,v8 在这个版本中定义了 41 种 elements 类型。这些 elements 究竟起到什么作用?这个在 谷歌的这篇 blog 中有讲到:
单纯从 JavaScript 的角度看,对象实际上就是就是以 string 作为 key ,任意值作为 value 的字典。当然在遍历的时候,情况会有差别。不过不同类型(string, number, symbol)的属性(key),的行为基本上是一致的(从字典的使用方式上来说)。但是出于性能和内存占用的考虑,V8 设计了不一样的属性类型。
其中,最显著的差别就在于,普通对象属性 和 数组下标 了。
举一个简单的例子:
1
2
3
|
const object = {first: "1", second: "2"};
const arr = ["1", "2"];
|
其中,object.first 和 object.second 是对象的属性(named property),而 1/2 属于是数组 arr 的元素(element),他们之间存在巨大差别。如图所示:
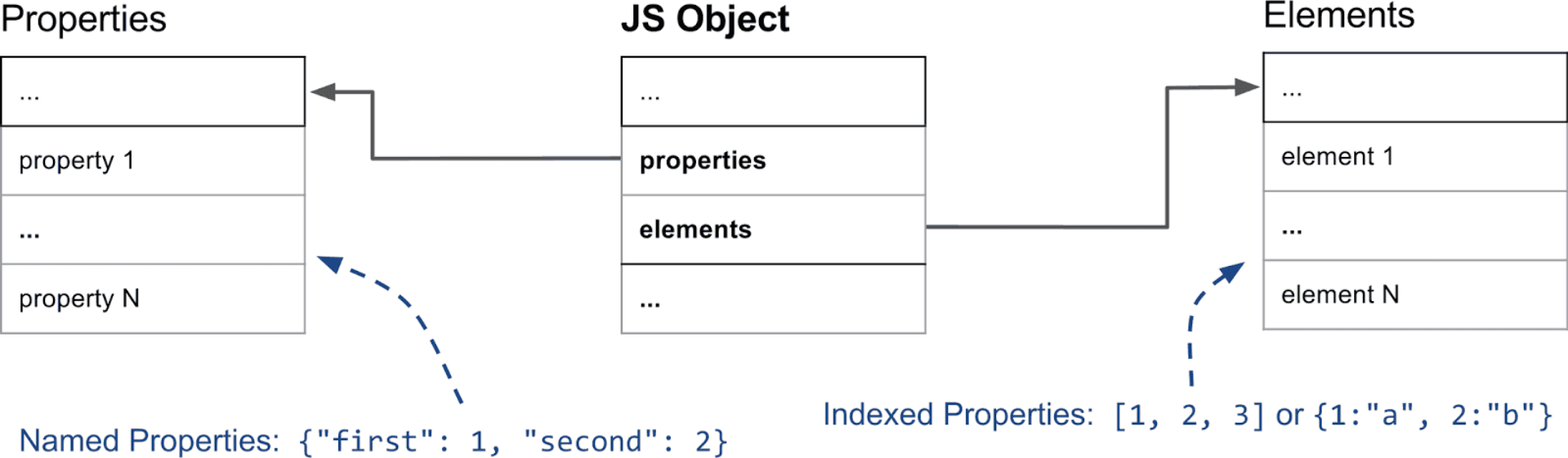
element 和 property 甚至不是使用一种数据结构进行存储。在 V8 的眼里,element 和 元素的属性是完全不同的两种东西。
下划线分割的三段说明了这些类型的三种基本层次。上文介绍的 element 属于是第一种层次,说明这些数据是元素类型。其他的两种见下文。
PACKED 和 HOLEY 这两种值,说明了数组当前是否是稀疏的(HOLEY)。
对于 V8 来说,这是两种存在重要差别的类型,一旦变为 HOLEY 意味着数组在之前的访问中发生了越界,数组中"有洞"了。这对于性能优化来说是一种负担。要知道在其他的语言中,数组越界是非常严重的错误,但是 js 不一样,js 认为数组越界访问不算什么大事,但是从 V8 的角度来看,数组越界如果是可以接受的,那么这种行为实际上根本没法控制,为了性能的考虑,只能用特殊的值来填补由于数组越界访问带来的“漏洞”。
例如:
1
2
|
const foo = [];
const foo[999] = 1;
|
这样的代码会带来什么后果? 如果 V8 老老实实,把 foo[999] 之前的 999 个空都分配好内存,这会带来什么样的后果?甚至更极端一些,如果不是 999 而是 99999999 呢?
所以出于性能上的考虑,HOLEY 的数组实际上处理起来要比 PACKED 的数组要多了判断条件,甚至可能触发原型链的查找。这会使得我们的数组操作变得极为缓慢。
- 第二段有三种值:
SMI 、 DOUBLE 和 ``
这三种值实际上应该被称为: smi double regular ,在 V8 中, smi 代表了小的整数,double 代表了浮点数和无法用 smi 代表的大整数,而 regular 代表的是普通元素,他们不能用 smi 或者 double 概括。从 smi -> double -> regular 属于是递进的关系,从 smi 到 regular,元素的类型变得越来越通用,而更通用类型的数组,是无法重新降级,变为更精确类型数组的。
来完成几个实验
说了那么多关于类型的东西,我们可以动动手在 Nodejs 交互式解释器 中中几个实验,看看数组在 V8 里面是怎么变化的。
- 给 node 传递一个 V8 引擎的参数:
--allow-natives-syntax,这样可以让我们直接使用到 V8 引擎提供的底层 api。
注 这么做主要是为了探究 V8 的部分,如果我们不传递这个 flag,那么像 %CollectGarbage() 这样的,以 % 开头的 V8 api 将无法调用,因为 js 不允许变量名以 %开头。
1
2
3
4
|
[picher@picherspc ~]$ node --allow-natives-syntax
Welcome to Node.js v16.13.0.
Type ".help" for more information.
>
|
- 操作数组,观察数组类型变化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
> arr.push(1)
1
> %DebugPrint(arr)
DebugPrint: 0x2fd1f4ffda51: [JSArray]
- map: 0x002db83835f1 <Map(PACKED_SMI_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties]
- prototype: 0x2a320a845af9 <JSArray[0]>
- elements: 0x0ec65dd20841 <FixedArray[17]> [PACKED_SMI_ELEMENTS]
- length: 1
- properties: 0x12ae6c281309 <FixedArray[0]>
- All own properties (excluding elements): {
0x12ae6c284d41: [String] in ReadOnlySpace: #length: 0x202b943c1189 <AccessorInfo> (const accessor descriptor), location: descriptor
}
- elements: 0x0ec65dd20841 <FixedArray[17]> {
0: 1
1-16: 0x12ae6c281669 <the_hole>
}
0x2db83835f1: [Map]
- type: JS_ARRAY_TYPE
- instance size: 32
- inobject properties: 0
- elements kind: PACKED_SMI_ELEMENTS
- unused property fields: 0
- enum length: invalid
- back pointer: 0x12ae6c281599 <undefined>
- prototype_validity cell: 0x202b943c15e9 <Cell value= 1>
- instance descriptors #1: 0x092220768279 <DescriptorArray[1]>
- transitions #2: 0x0172c20afc81 <TransitionArray[8]>Transition array #2:
0x172c20acd49: [String] in OldSpace: #level: (transition to (const data field, attrs: [WEC]) @ Any) -> 0x2fe087e07851 <Map(PACKED_SMI_ELEMENTS)>
0x12ae6c285949 <Symbol: (elements_transition_symbol)>: (transition to HOLEY_SMI_ELEMENTS) -> 0x002db83835a9 <Map(HOLEY_SMI_ELEMENTS)>
- prototype: 0x2a320a845af9 <JSArray[0]>
- constructor: 0x3c9fb29cdba9 <JSFunction Array (sfi = 0x3299fbc5ec79)>
- dependent code: 0x12ae6c281239 <Other heap object (WEAK_FIXED_ARRAY_TYPE)>
- construction counter: 0
[ 1 ]
|
我们主要看后半段的详细信息,输出显示元素的类型是: PACKED_SMI_ELEMENTS:
1
|
- elements kind: PACKED_SMI_ELEMENTS
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
> arr.push(10.24)
2
> %DebugPrint(arr)
DebugPrint: 0x3cdbba546781: [JSArray] in OldSpace
- map: 0x002db8383561 <Map(PACKED_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties]
- prototype: 0x2a320a845af9 <JSArray[0]>
- elements: 0x1e684e5693f9 <FixedDoubleArray[17]> [PACKED_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS]
- length: 2
- properties: 0x12ae6c281309 <FixedArray[0]>
- All own properties (excluding elements): {
0x12ae6c284d41: [String] in ReadOnlySpace: #length: 0x202b943c1189 <AccessorInfo> (const accessor descriptor), location: descriptor
}
- elements: 0x1e684e5693f9 <FixedDoubleArray[17]> {
0: 1
1: 10.24
2-16: <the_hole>
}
0x2db8383561: [Map]
- type: JS_ARRAY_TYPE
- instance size: 32
- inobject properties: 0
- elements kind: PACKED_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS
- unused property fields: 0
- enum length: invalid
- back pointer: 0x002db83835a9 <Map(HOLEY_SMI_ELEMENTS)>
- prototype_validity cell: 0x202b943c15e9 <Cell value= 1>
- instance descriptors #1: 0x3cdbba546899 <DescriptorArray[2]>
- transitions #1: 0x2a320a8461f9 <TransitionArray[4]>Transition array #1:
0x12ae6c285949 <Symbol: (elements_transition_symbol)>: (transition to HOLEY_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS) -> 0x002db8383519 <Map(HOLEY_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS)>
- prototype: 0x2a320a845af9 <JSArray[0]>
- constructor: 0x3c9fb29cdba9 <JSFunction Array (sfi = 0x3299fbc5ec79)>
- dependent code: 0x12ae6c281239 <Other heap object (WEAK_FIXED_ARRAY_TYPE)>
- construction counter: 0
[ 1, 10.24 ]
|
此时显示数组的元素类型是: PACKED_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS:
1
|
- elements kind: PACKED_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
> arr.push('foo')
3
> %DebugPrint(arr)
DebugPrint: 0x3cdbba546781: [JSArray] in OldSpace
- map: 0x002db8383441 <Map(PACKED_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties]
- prototype: 0x2a320a845af9 <JSArray[0]>
- elements: 0x0ec65dd1d8c9 <FixedArray[17]> [PACKED_ELEMENTS]
- length: 3
- properties: 0x12ae6c281309 <FixedArray[0]>
- All own properties (excluding elements): {
0x12ae6c284d41: [String] in ReadOnlySpace: #length: 0x202b943c1189 <AccessorInfo> (const accessor descriptor), location: descriptor
}
- elements: 0x0ec65dd1d8c9 <FixedArray[17]> {
0: 0x0ec65dd1d971 <HeapNumber 1.0>
1: 0x0ec65dd1d961 <HeapNumber 10.24>
2: 0x21ef98e561f1 <String[3]: #foo>
3-16: 0x12ae6c281669 <the_hole>
}
0x2db8383441: [Map]
- type: JS_ARRAY_TYPE
- instance size: 32
- inobject properties: 0
- elements kind: PACKED_ELEMENTS
- unused property fields: 0
- enum length: invalid
- back pointer: 0x002db8383519 <Map(HOLEY_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS)>
- prototype_validity cell: 0x202b943c15e9 <Cell value= 1>
- instance descriptors #1: 0x3cdbba546899 <DescriptorArray[2]>
- transitions #4: 0x10313dc14e11 <TransitionArray[12]>Transition array #4:
0x3cdbba5554d9: [String] in OldSpace: #level: (transition to (const data field, attrs: [WEC]) @ Any) -> 0x2fe087e0b9d9 <Map(PACKED_ELEMENTS)>
0x12ae6c285949 <Symbol: (elements_transition_symbol)>: (transition to HOLEY_ELEMENTS) -> 0x002db8383639 <Map(HOLEY_ELEMENTS)>
0x12ae6c285241: [String] in ReadOnlySpace: #raw: (transition to (const data field, attrs: [___]) @ Any) -> 0x002db83bac29 <Map(PACKED_ELEMENTS)>
0x12ae6c2859a9 <Symbol: (frozen_symbol)>: (transition to frozen) -> 0x002db8383681 <Map(PACKED_FROZEN_ELEMENTS)>
- prototype: 0x2a320a845af9 <JSArray[0]>
- constructor: 0x3c9fb29cdba9 <JSFunction Array (sfi = 0x3299fbc5ec79)>
- dependent code: 0x12ae6c281239 <Other heap object (WEAK_FIXED_ARRAY_TYPE)>
- construction counter: 0
[ 1, 10.24, 'foo' ]
|
此时显示数组的元素类型是: PACKED_ELEMENTS:
1
|
- elements kind: PACKED_ELEMENTS
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
> arr[9] = 'bar'
'bar'
> %DebugPrint(arr)
DebugPrint: 0x3cdbba546781: [JSArray] in OldSpace
- map: 0x002db8383639 <Map(HOLEY_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties]
- prototype: 0x2a320a845af9 <JSArray[0]>
- elements: 0x3bb3582411e1 <FixedArray[17]> [HOLEY_ELEMENTS]
- length: 10
- properties: 0x12ae6c281309 <FixedArray[0]>
- All own properties (excluding elements): {
0x12ae6c284d41: [String] in ReadOnlySpace: #length: 0x202b943c1189 <AccessorInfo> (const accessor descriptor), location: descriptor
}
- elements: 0x3bb3582411e1 <FixedArray[17]> {
0: 0x3bb3582412a9 <HeapNumber 1.0>
1: 0x3bb3582412b9 <HeapNumber 10.24>
2: 0x21ef98e561f1 <String[3]: #foo>
3-8: 0x12ae6c281669 <the_hole>
9: 0x21ef98e70fe1 <String[3]: #bar>
10-16: 0x12ae6c281669 <the_hole>
}
0x2db8383639: [Map]
- type: JS_ARRAY_TYPE
- instance size: 32
- inobject properties: 0
- elements kind: HOLEY_ELEMENTS
- unused property fields: 0
- enum length: invalid
- stable_map
- back pointer: 0x002db8383441 <Map(PACKED_ELEMENTS)>
- prototype_validity cell: 0x202b943c15e9 <Cell value= 1>
- instance descriptors (own) #1: 0x092220768279 <DescriptorArray[1]>
- prototype: 0x2a320a845af9 <JSArray[0]>
- constructor: 0x3c9fb29cdba9 <JSFunction Array (sfi = 0x3299fbc5ec79)>
- dependent code: 0x12ae6c281239 <Other heap object (WEAK_FIXED_ARRAY_TYPE)>
- construction counter: 0
[ 1, 10.24, 'foo', <6 empty items>, 'bar' ]
|
我们看到,界外访问之后,数组的元素类型变成了: HOLEY_ELEMENTS:
1
|
- elements kind: HOLEY_ELEMENTS
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
> arr[32 << 20] = 0;
0
> %DebugPrint(arr)
DebugPrint: 0x3cdbba546781: [JSArray] in OldSpace
- map: 0x002db8381869 <Map(DICTIONARY_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties]
- prototype: 0x2a320a845af9 <JSArray[0]>
- elements: 0x3e5557730419 <NumberDictionary[52]> [DICTIONARY_ELEMENTS]
- length: 33554433
- properties: 0x12ae6c281309 <FixedArray[0]>
- All own properties (excluding elements): {
0x12ae6c284d41: [String] in ReadOnlySpace: #length: 0x202b943c1189 <AccessorInfo> (const accessor descriptor), location: descriptor
}
- elements: 0x3e5557730419 <NumberDictionary[52]> {
- max_number_key: 33554432
33554432: 0 (data, dict_index: 0, attrs: [WEC])
2: 0x21ef98e561f1 <String[3]: #foo> (data, dict_index: 0, attrs: [WEC])
9: 0x21ef98e70fe1 <String[3]: #bar> (data, dict_index: 0, attrs: [WEC])
0: 0x3bb3582412a9 <HeapNumber 1.0> (data, dict_index: 0, attrs: [WEC])
1: 0x3bb3582412b9 <HeapNumber 10.24> (data, dict_index: 0, attrs: [WEC])
20: 0x21ef98e76fa9 <String[4]: #bar1> (data, dict_index: 0, attrs: [WEC])
}
0x2db8381869: [Map]
- type: JS_ARRAY_TYPE
- instance size: 32
- inobject properties: 0
- elements kind: DICTIONARY_ELEMENTS
- unused property fields: 0
- enum length: invalid
- stable_map
- back pointer: 0x002db8383639 <Map(HOLEY_ELEMENTS)>
- prototype_validity cell: 0x202b943c15e9 <Cell value= 1>
- instance descriptors (own) #1: 0x092220768279 <DescriptorArray[1]>
- prototype: 0x2a320a845af9 <JSArray[0]>
- constructor: 0x3c9fb29cdba9 <JSFunction Array (sfi = 0x3299fbc5ec79)>
- dependent code: 0x12ae6c281239 <Other heap object (WEAK_FIXED_ARRAY_TYPE)>
- construction counter: 0
[
1,
10.24,
'foo',
<6 empty items>,
'bar',
<10 empty items>,
'bar1',
<33554411 empty items>,
0
]
|
在试图插入一个超出数组边界非常多的元素时,数组的元素类型变成了: DICTIONARY_ELEMENTS:
1
|
- elements kind: DICTIONARY_ELEMENTS
|
经过以上几个实验,我们观察到,在 V8 的实现中,数组的类型,发生了质的改变,这些信息在 JavaScript 的层面上是完全透明的,V8 隐藏了这些细节。
v8 数组的核心源码
上文我们通过几步实验,验证了 V8 层面的数组类型变化。我们接下来正式进入主题,看看源码长什么样子:)
经过上文分析可以得出的结论是: V8 会在新建和增加数组元素时进行数组元素类型的转换。下面我们就以增加数组元素为例,阅读一下 V8 的核心源码部分:
增加数组元素
V8 关于数组元素操作的代码主要封装在 JSArray 这个类里面。在 js-array.h
源代码的注释里说明了 js 数组的两种实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
// The JSArray describes JavaScript Arrays
// Such an array can be in one of two modes:
// - fast, backing storage is a FixedArray and length <= elements.length();
// Please note: push and pop can be used to grow and shrink the array.
// - slow, backing storage is a HashTable with numbers as keys.
class JSArray : public JSObject {
|
JSArray 实际上是 JSObject 的派生类,因此我们继续看 JSObject 的实现。
在 JSObject 的头文件中可以找到添加元素的函数签名:
1
2
3
|
V8_EXPORT_PRIVATE static Maybe<bool> AddDataElement(
Handle<JSObject> receiver, uint32_t index, Handle<Object> value,
PropertyAttributes attributes);
|
我们知道
我们来看看函数的定义部分:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
Maybe<bool> JSObject::AddDataElement(Handle<JSObject> object, uint32_t index,
Handle<Object> value,
PropertyAttributes attributes) {
Isolate* isolate = object->GetIsolate();
DCHECK(object->map(isolate).is_extensible());
uint32_t old_length = 0;
uint32_t new_capacity = 0;
if (object->IsJSArray(isolate)) {
CHECK(JSArray::cast(*object).length().ToArrayLength(&old_length));
}
ElementsKind kind = object->GetElementsKind(isolate);
FixedArrayBase elements = object->elements(isolate);
ElementsKind dictionary_kind = DICTIONARY_ELEMENTS;
if (IsSloppyArgumentsElementsKind(kind)) {
elements = SloppyArgumentsElements::cast(elements).arguments(isolate);
dictionary_kind = SLOW_SLOPPY_ARGUMENTS_ELEMENTS;
} else if (IsStringWrapperElementsKind(kind)) {
dictionary_kind = SLOW_STRING_WRAPPER_ELEMENTS;
}
if (attributes != NONE) {
kind = dictionary_kind;
} else if (elements.IsNumberDictionary(isolate)) {
kind = ShouldConvertToFastElements(
*object, NumberDictionary::cast(elements), index, &new_capacity)
? BestFittingFastElementsKind(*object)
: dictionary_kind;
} else if (ShouldConvertToSlowElements(
*object, static_cast<uint32_t>(elements.length()), index,
&new_capacity)) {
kind = dictionary_kind;
}
ElementsKind to = value->OptimalElementsKind(isolate);
if (IsHoleyElementsKind(kind) || !object->IsJSArray(isolate) ||
index > old_length) {
to = GetHoleyElementsKind(to);
kind = GetHoleyElementsKind(kind);
}
to = GetMoreGeneralElementsKind(kind, to);
ElementsAccessor* accessor = ElementsAccessor::ForKind(to);
MAYBE_RETURN(accessor->Add(object, index, value, attributes, new_capacity),
Nothing<bool>());
if (object->IsJSArray(isolate) && index >= old_length) {
Handle<Object> new_length =
isolate->factory()->NewNumberFromUint(index + 1);
JSArray::cast(*object).set_length(*new_length);
}
return Just(true);
}
|
可以看到,代码主要分为了以下步骤:
- 检查是否是可添加元素的数组
- 检查是否是数组,如果是则获取当前数组长度
- 获取当前数组的元素类型
- 预先准备好可以转换到的字典元素类型
- 根据条件检查正确且最优的元素转换类型,并赋值给
kind
- 获取即将添加的值
value 的最优的元素类型并赋值给 to
- 如果发现数组可能会便稀疏,则
to 和 kind 会被重新赋予相应的 HOLEY 类型
- 从
kind 和 to 中选择最宽泛的类型,并赋值给 to
- 获取一个类型为
to 的 accessor
- 尝试添加元素
- 如果扩容后仍然是数组,且数组大小变大,数组重新设置长度值
小结
- JS 数组在 V8 中使用特殊的数据结构
element 保存。
- 数组大小在一定范围内: ~268MB 时,会使用 FixedArray 存放数据,并且会非常高效(相对 JS 的字典类型而言)。一旦数组可能变得非常大,V8 会转而使用字典类型存放数组数据。
- 数组的扩容,在一定范围内是自动发生的。
- JS 的数组具有类型,每一个数组都会有一个这样的类型。
- JS 的数组类型会在插入不同数据、不同操作的时候发生转变。
- 尽量使用更精确的 JS 数据类型,这样会使得 V8 更加高效。
文献引用

